In previous blog we have seen if our primary router goes down backup router will provide redundancy. But there is some other possibility also.
Here R1 and R2 are client side router connected to R3 (ISP) router. R1 working as a Primary and R2 working as a secondary. Now what if "S1/1" of R3 goes down and still we don't have any configuration for this. So according to our previous configuration R1 still act like Primary. So with help of HSRP we can track our interfaces also.
Configuration-
R1(config)#int s 1/1
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config)#int f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip add 192.168.1.1 //Virtual ip
R1(config-if)#standby 1 priority 105 // Making Primary
R1(config-if)#standby 1 preempt
R1(config-if)#standby 1 track serial 1/1
and on R2-
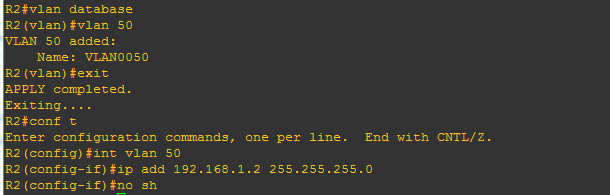
R2(config)#int s 1/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config)#int f0/1
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip add 192.168.1.1 //Virtual ip
R1(config-if)#standby 1 priority 100 //Making Secondary
R1(config-if)#standby 1 preempt
R1(config-if)#standby 1 track serial 1/0
Now go on R3 and shutdown S1/1. You'll R2 will become Primary.
Here R1 and R2 are client side router connected to R3 (ISP) router. R1 working as a Primary and R2 working as a secondary. Now what if "S1/1" of R3 goes down and still we don't have any configuration for this. So according to our previous configuration R1 still act like Primary. So with help of HSRP we can track our interfaces also.
Configuration-
R1(config)#int s 1/1
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config)#int f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip add 192.168.1.1 //Virtual ip
R1(config-if)#standby 1 priority 105 // Making Primary
R1(config-if)#standby 1 preempt
R1(config-if)#standby 1 track serial 1/1
and on R2-
R2(config)#int s 1/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config)#int f0/1
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#standby 1 ip add 192.168.1.1 //Virtual ip
R1(config-if)#standby 1 priority 100 //Making Secondary
R1(config-if)#standby 1 preempt
R1(config-if)#standby 1 track serial 1/0
Now go on R3 and shutdown S1/1. You'll R2 will become Primary.