VRRP- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
I have written about HSRP in previous post. Today I am going to write on VRRP.
There are 3 main benefits to using VRRP over HSRP.
1.Open Standard (We can use any vendor's router)
2.Faster then HSRP
3.No need to give ip of any virtual router.
In VRRP we'll give ip of a router interface. So that router which interface we are going to use for VRRP will become Master.And there is no preemption because by default Master router have maximum priority (255) and Backup have 100. So if someone configure priority 255 of backup it'll not coop to become Master.
Topology--
Simplest topology ever. 2 router (3600 Series) with a Ether Switch Module installed (NM-16ESW). 1 switch and one cloud in which I have configured loopback(ip-192.168.1.100 192.168.1.100 and gateway 192.168.1.1) interface by this I can communicate from my PC.
192.168.1.100 and gateway 192.168.1.1) interface by this I can communicate from my PC.
Configuration-
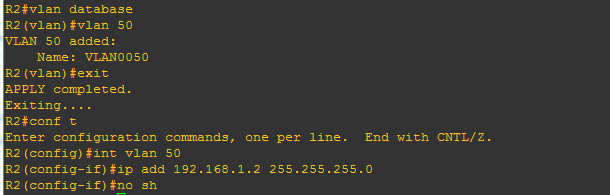
1.Create vlan-50 on both router and give ip-
2.Now make Fast Ethernet member of VLAN-50--
R1(config)#int ran f 1/0 - 1
R1(config-if - range)#switchport mode access
R1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 50
and same on R2
R2(config)#int ran f 1/0 - 1
R2(config-if - range)#switchport mode access
R2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 50
3.Now configure VRRP on both Routers---
R1(config)#int vlan 50
R1(config-vlan)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
After this command you will get a message-
"*Mar 1 00:01:08.439: %VRRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vl50 Grp 1 state Init -> Master"
It means your router become Master now time to configure R2 as R1-
R2(config)#int vlan 50
R2(config-vlan)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
And after this command you will get a message-
"*Mar 1 00:01:06.283: %VRRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vl50 Grp 1 state Master -> Backup "
It means your R2 become Backup.
Testing-
To see vrrp Configuration type
R1#show vrrp
Now try to ping 192.168.1.1 from you pc.
On R1 you will see a message--
I have written about HSRP in previous post. Today I am going to write on VRRP.
There are 3 main benefits to using VRRP over HSRP.
1.Open Standard (We can use any vendor's router)
2.Faster then HSRP
3.No need to give ip of any virtual router.
In VRRP we'll give ip of a router interface. So that router which interface we are going to use for VRRP will become Master.And there is no preemption because by default Master router have maximum priority (255) and Backup have 100. So if someone configure priority 255 of backup it'll not coop to become Master.
Topology--
Simplest topology ever. 2 router (3600 Series) with a Ether Switch Module installed (NM-16ESW). 1 switch and one cloud in which I have configured loopback(ip-192.168.1.100
 192.168.1.100 and gateway 192.168.1.1) interface by this I can communicate from my PC.
192.168.1.100 and gateway 192.168.1.1) interface by this I can communicate from my PC.Configuration-
1.Create vlan-50 on both router and give ip-
2.Now make Fast Ethernet member of VLAN-50--
R1(config)#int ran f 1/0 - 1
R1(config-if - range)#switchport mode access
R1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 50
and same on R2
R2(config)#int ran f 1/0 - 1
R2(config-if - range)#switchport mode access
R2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 50
3.Now configure VRRP on both Routers---
R1(config)#int vlan 50
R1(config-vlan)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
After this command you will get a message-
"*Mar 1 00:01:08.439: %VRRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vl50 Grp 1 state Init -> Master"
It means your router become Master now time to configure R2 as R1-
R2(config)#int vlan 50
R2(config-vlan)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
And after this command you will get a message-
"*Mar 1 00:01:06.283: %VRRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vl50 Grp 1 state Master -> Backup "
It means your R2 become Backup.
Testing-
To see vrrp Configuration type
R1#show vrrp
And to see configuration on R2 same command
Now try to ping 192.168.1.1 from you pc.
It is successful. Now shutdown vlan interface of R1 (On which we have configured 192.168.1.1).
On R1 you will see a message--
And on R2-
So now your R2 become Master, now try to ping 192.168.1.1 again from pc--
And still you can see that we are able to ping.